Methane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%) This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution , coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips It lasts an average of 12 years in the atmosphereThat's exactly how greenhouse gases act They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere Overall, greenhouse gases are a good thing Without them, our planet would be too cold, and life as we know it would not exist But there can be too much of a good thing Scientists are worriedGreenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warming
The Greenhouse Gas No One S Talking About Nitrous Oxide On Farms Explained Civil Eats
Right amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
Right amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere-The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming itGreenhouse gas emissions and atmospheric concentrations have increased over the past 150 years Emissions of several important greenhouse gases that result from human activity have increased substantially since largescale industrialization began in the mid1800s Most of these humancaused (anthropogenic) greenhouse gas emissions were carbon dioxide (CO2)



3
The greenhouse effect Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere , the Earth would be about 18°C colder on average than it is now That would make it too cold to support life as we know itAs you might expect, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide are the most abundant greenhouse gases in our atmosphere If we take carbon dioxide (CO2) as an example, concentrations of the gas have risen by around 40% since the Industrial RevolutionSulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) is an extremely potent greenhouse gas SF 6 is very persistent, with an atmospheric lifetime of more than a thousand years Thus, a relatively small amount of SF 6 can have a significant longterm impact on global climate change SF 6 is humanmade, and the primary user of SF 6 is the electric power industry Because of its inertness and dielectric properties, it is
Greenhouse gas molecules in the atmosphere absorb light, preventing some of it from escaping the Earth This heats up the atmosphere and raises the planet's average temperature What do CO2, methane, and water vapor have in common?But if the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere changes, the strength of the greenhouse effect changes too This is the cause of humanmade climate change by adding greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, we are trapping more heat, and the entire planet gets warmer The focus on "carbon" For climate change, the most important greenhouse gas isThe greenhouse gas index is based on precise measurements of gases in the atmosphere, which are collected from a network of sites around the globe and analyzed at NOAA's Earth System Research Lab in Boulder, Colorado The index is proportional to the change in the direct climatewarming influence (also known as climate forcing) exerted by five primary greenhouse gases
Due to human intervention, the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has increased remarkably causing the greenhouse effect Greenhouse Gases Names The energy coming from the sun is either reflected, transmitted or trapped by Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases trap energy at longer wavelengths, ie infrared regions and increase the temperature Greenhouse gasesMethane, by contrast, is mostly removed from the atmosphere by chemical reaction, persisting for about 12 years Thus although methane is a potent greenhouse gas, its effect is relatively shortlivedCarbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels is the largest single source of greenhouse gas emissions from human activities The supply and use of fossil fuels accounts for about three quarters of mankind's carbon dioxide (CO 2) emissions (equal to some 59 billion metric tonnes of carbon in 1992), onefifth of the methane (CH 4), and a significant quantity of nitrous oxide (N 2
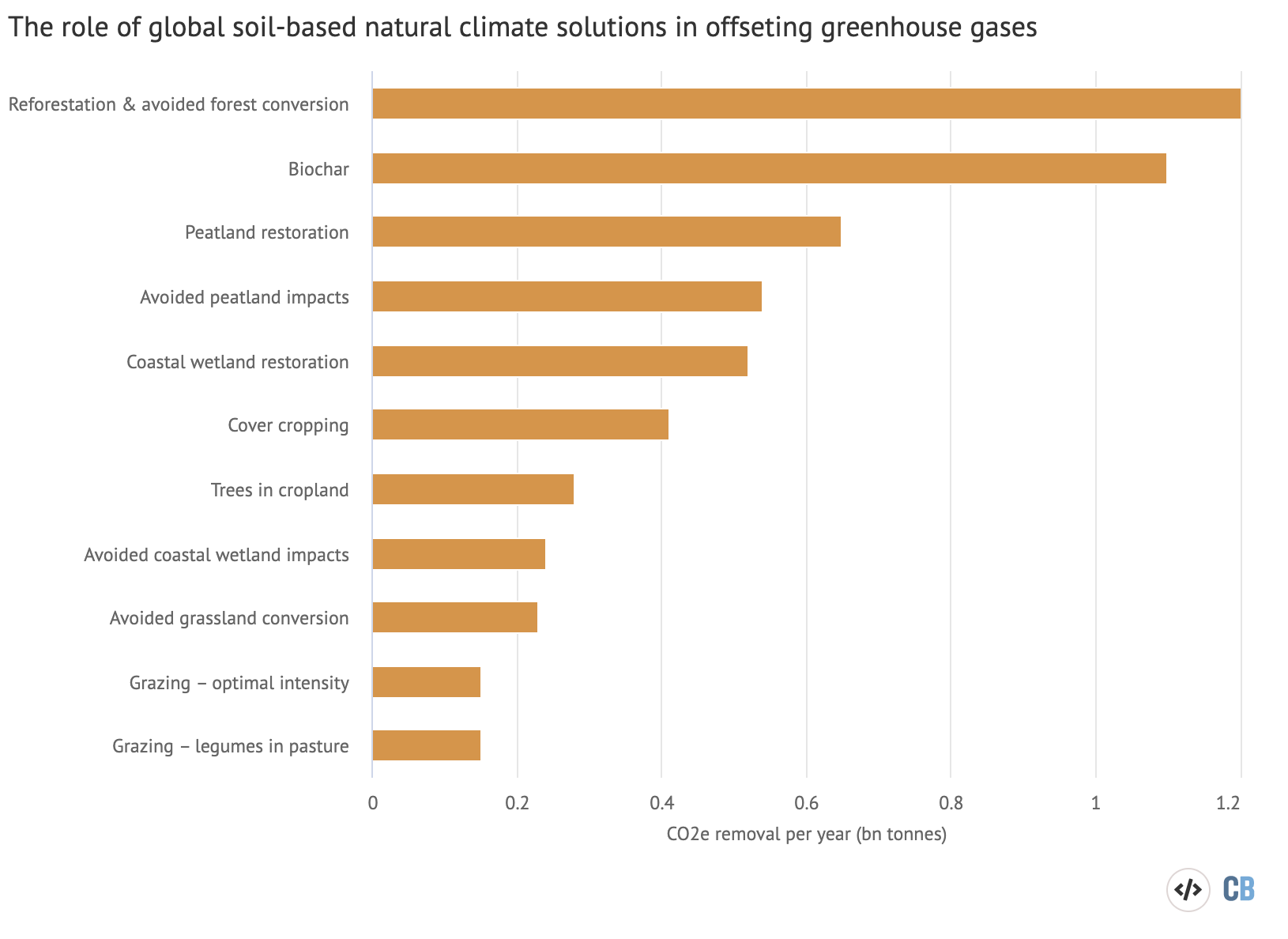



Restoring Soils Could Remove Up To 5 5bn Tonnes Of Greenhouse Gases Every Year




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
The three most important greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4) and nitrous oxide (N 2 O) While carbon dioxide is the greenhouse gas we hear the most about, methane and nitrous oxide have greater global warming potential (GWP) Methane has a GWP of 25 for a 100year period and nitrous oxide has a GWP of 298 For mostBut the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has skyrocketed to detrimental levels in recent history Related Carbon dioxide soars to record breaking levels not seen in at least 800,000 yearsGases in air The air is a mixture of gases The amount of water vapour in the air varies from place to place, and day to day For this reason, the proportions of the gases in the air are usually
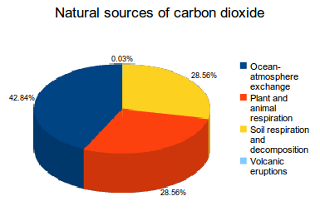



Main Sources Of Carbon Dioxide Emissions What S Your Impact



Main Sources Of Carbon Dioxide Emissions What S Your Impact
Greenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide is the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect The major contributors to the greenhouses gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation , etc The increased number of factories and automobiles increases the amount of these gases in the atmosphereThe atmosphere of Earth, commonly known as air, is the layer of gases retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphereThe atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effectHuman activities and the greenhouse effect Human activities are increasing the amount of some greenhouse gases in the atmosphere For example farming cattle releases methane



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
Greenhouse effect Some thermal energy from the Earth's surface escapes into space If too much thermal energy escaped, the planet would be very cold However some gases in the atmosphereSince the Industrial Revolution began in the 1700s, people have added a substantial amount of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels, cutting down forests, and conducting other activities (see the US and Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions indicators) When greenhouse gases are emitted into the atmosphere, many remain there for long timeMain Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived



Co2 Makes Up Just 0 04 Of Earth S Atmosphere Here S Why Its Impact Is So Massive




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
A greenhouse gas is a gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation This is causing a greenhouse effect, and the resultant warming of the earth's surface to a temperature above its normal temperature range The radiation is released and redirect towards the earth surface depends on a number of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere GreenhouseThe carbon cycle's sinks and sources help to regulate the amount of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere Greenhouse Gases Besides CO 2 there are other greenhouse gases These include water vapor, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Without any greenhouse gases, Earth would be an icy wasteland Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding ontoCarbon dioxide (004%), nitrous oxide, methane, and ozone are trace gases that account for almost 01% of Earth's atmosphere and have an appreciable greenhouse effect In order, the most abundant greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are Water vapor (H 2O)



Gml Noaa Gov Education Info Activities Pdfs Cta The Methane Cycle Pdf




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
The excess of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is triggering harmful global warming, so reducing the amount of these gases should help to tackle climate change This can be done in two ways lower the emissions we are sending into the atmosphere, from activities such as industrial processes, power generation, transport and intensive agriculture;The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbonsScientists generally divide these helpful actions (known as " climate change mitigation ") into three categories reducing CO 2 and other harmful greenhouse gas emissions (the release of these gases into the atmosphere), reducing the amount of sunlight that reaches the earth's surface, or removing CO 2 from the atmosphere Each of these actions has different costs,




Percentage Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Download Scientific Diagram



1
Nearly all have reached the same conclusion if we increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the Earth will warm up What they don't agree on is by how much This issue is called 'climate sensitivity', the amount the temperatures will increase if CO2 is doubled from preindustrial levels Climate models have predicted the least temperature riseGreenhouse gases arise naturally, and are part of the makeup of our atmosphere Earth is sometimes called the "Goldilocks" planet – it's not too hot, not too cold, and the conditions are just right to allow life, including us, to flourish Part of what makes Earth so amenable is the naturallyarising greenhouse effect, which keeps the planet at a friendly 15Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, in a process called the "greenhouse effect



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature




Percentage Share Of Greenhouse Gases In The Earth Atmosphere 5 Download Scientific Diagram
Unlike oxygen or nitrogen (which make up most of our atmosphere), greenhouse gases absorb that heat and release it gradually over time, like bricks in a fireplace after the fire goes out Without this natural greenhouse effect, Earth's average annual temperature would be below freezing instead of close to 60°F But increases in greenhouse gases have tipped the Earth's energyVolcanoes—both on land and under the ocean—release greenhouse gases, so periods of high volcanic activity tend to be warmer Since the Industrial Revolution of the late 1700s and early 1800s, people have been releasing larger quantities of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere That amount has skyrocketed in the past centuryBecause many of the major greenhouse gases stay in the atmosphere for tens to hundreds of years after being released, their warming effects on the climate persist over a long time and can therefore affect both present and future generations Summary of Key Points US Greenhouse Gas Emissions In the United States, greenhouse gas emissions caused by human activities




The Greenhouse Gas No One S Talking About Nitrous Oxide On Farms Explained Civil Eats
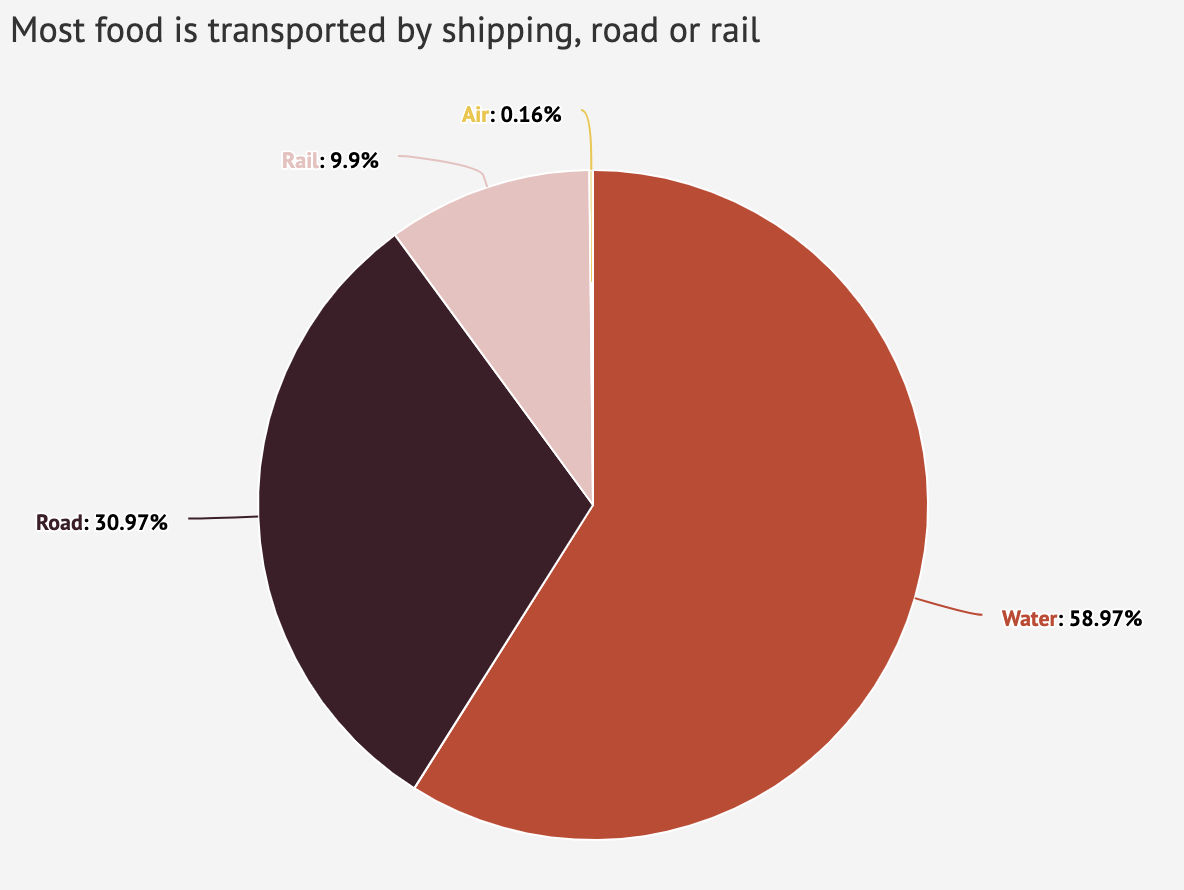



Interactive What Is The Climate Impact Of Eating Meat And Dairy Carbon Brief
The answer lies in the greenhouse effect — gases in our atmosphere (including CO 2, CH 4 (methane) and H 2 O water vapor) trap much of the emitted heat and then reradiate it back to Earth's surface This means that the energy leaving our planet from the top of the atmosphere is less than one would expect given the known temperature of our planet As mentioned earlier, this effectFor example, the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere and the amount of CO 2 dissolved in surface waters of the oceans stay in equilibrium, because the air and water mix well at the sea surface When we add more CO 2 to the atmosphere, a proportion of it dissolves into the oceans Anthropogenic greenhouse gases Since the start of the Industrial Revolution in theGreenhouse gases, including the carboncontaining gases carbon dioxide and methane, Due to humans' heavy reliance on fossil fuels, energy usage, and constant deforestation, the amount of greenhouse gas in the atmosphere is increasing, which makes reducing a greenhouse gas footprint harder to achieve However, there are several ways to reduce one's greenhouse gas




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems



3
Greenhouse gases include gases such as carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gasesThese greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto the Earth's surface Then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from the surface inside Earth's atmosphereThe gases act like the glass walls of a greenhouse"The problem is that our emissions went back up again and so we didn't really see a noticeable change in the total amount of greenhouse gases and the concentration in the atmosphere," Hill saidGreenhouses gases are atmospheric gases such as carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), and water vapor (H 2 O) that absorb and reradiate heat, which warms the lower atmosphere and Earth's surfaceThis process of absorption and reradiation of heat is called the greenhouse effectAlthough greenhouse gases only make up a small percentage of the atmosphere, small changes in the amount
_1050_718_s_c1_c_c.jpg)



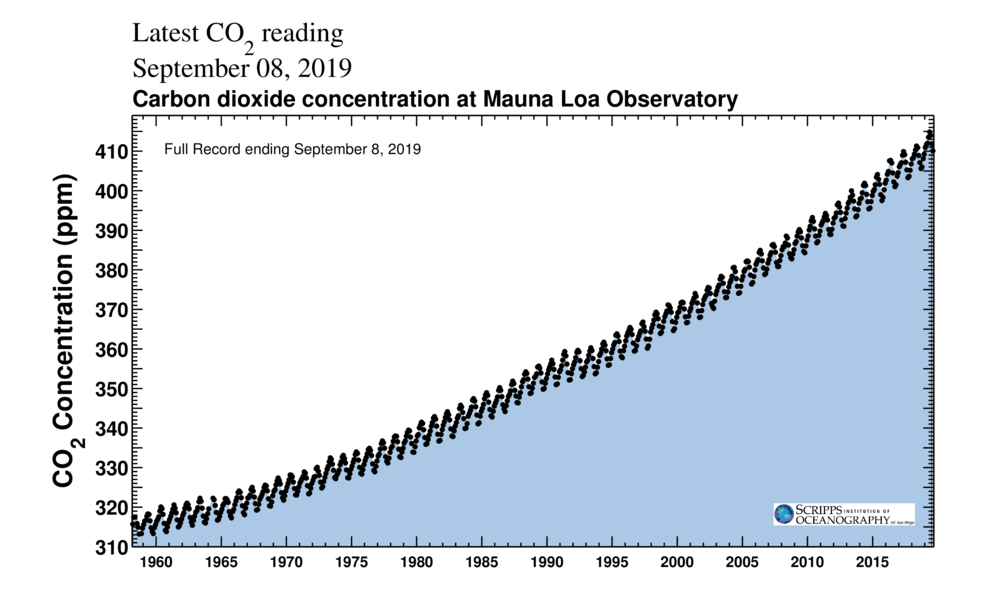
Carbon Dioxide Is Rising At Record Rates Climate Central




Carbon Dioxide In Earth S Atmosphere Wikipedia
The more people growing their own plants, food and trees, the higher amount of greenhouse gases we can eliminate from the air A food mile represents a mile which the food has to be transported from producer to consumer, some foods have huge food miles These miles are often made by large semitrucks that release a multitude of chemicals into the atmosphereThe amount of carbon dioxide is 3×10 18 grams These figures are converted into mole by dividing by the molecular weight in grams The molecular weight of H 2 O is approximately 18 and that of CO 2 is 44 Thus the moles of the two substances in theLarger emissions of greenhouse gases lead to higher concentrations in the atmosphere Greenhouse gas concentrations are measured in parts per million, parts per billion, and even parts per trillion One part per million is equivalent to one drop of water diluted into about 13 gallons of liquid (roughly the fuel tank of a compact car)




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate



Greenhouse Gases Climate Aware
As the planet gets warmer, more water evaporates from the Earth's surface and becomes vapor in the atmosphere Water vapor is a greenhouse gas, so more water vapor in the atmosphere leads to even more warming This is an example of a positive feedback loop, which happens when warming causes changes that lead to even more warming Alternative version for screen readerSince the Industrial Revolution in the late 1700s and early 1800s, people have been releasing large quantities of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere That amount has skyrocketed in the past century Greenhouse gas emissions increased 70 percent between 1970 and 04 Emissions of carbon dioxide, the most important greenhouse gas, rose byLike other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight Unlike those more abundant gases though, greenhouse gases are not transparent to heat (longwave infrared radiation) The sunwarmed surface of Earth radiates heat day and night Some heat escapes freely to space, but some is absorbed by greenhouse gas




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases Greenhouse gasesIf your first thought was "greenhouse gases," you'd be correct!To stop climate change, we need to stop the amount of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, from increasingFor the past 150 years, burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests, which naturally pull carbon dioxide out of the air, has caused greenhouse gas levels to increase There are two main ways to stop the amount of greenhouse gases from increasing we can stop



6 Major Types Of Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Atmosphere Wikiever



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight At night, Earth's surface coolsThe greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary atmosphere warms the planet's surface beyond the temperature it would have in the absence of its atmosphere Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth's temperature would be about −18 °C (−04 °F) compared to Earth's actual surface temperature of approximately 14 °C (572 °F)
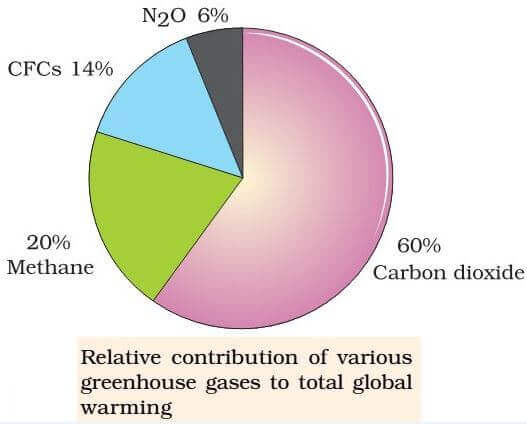



Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias




Global Carbon Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Untitled Document



The Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Effect
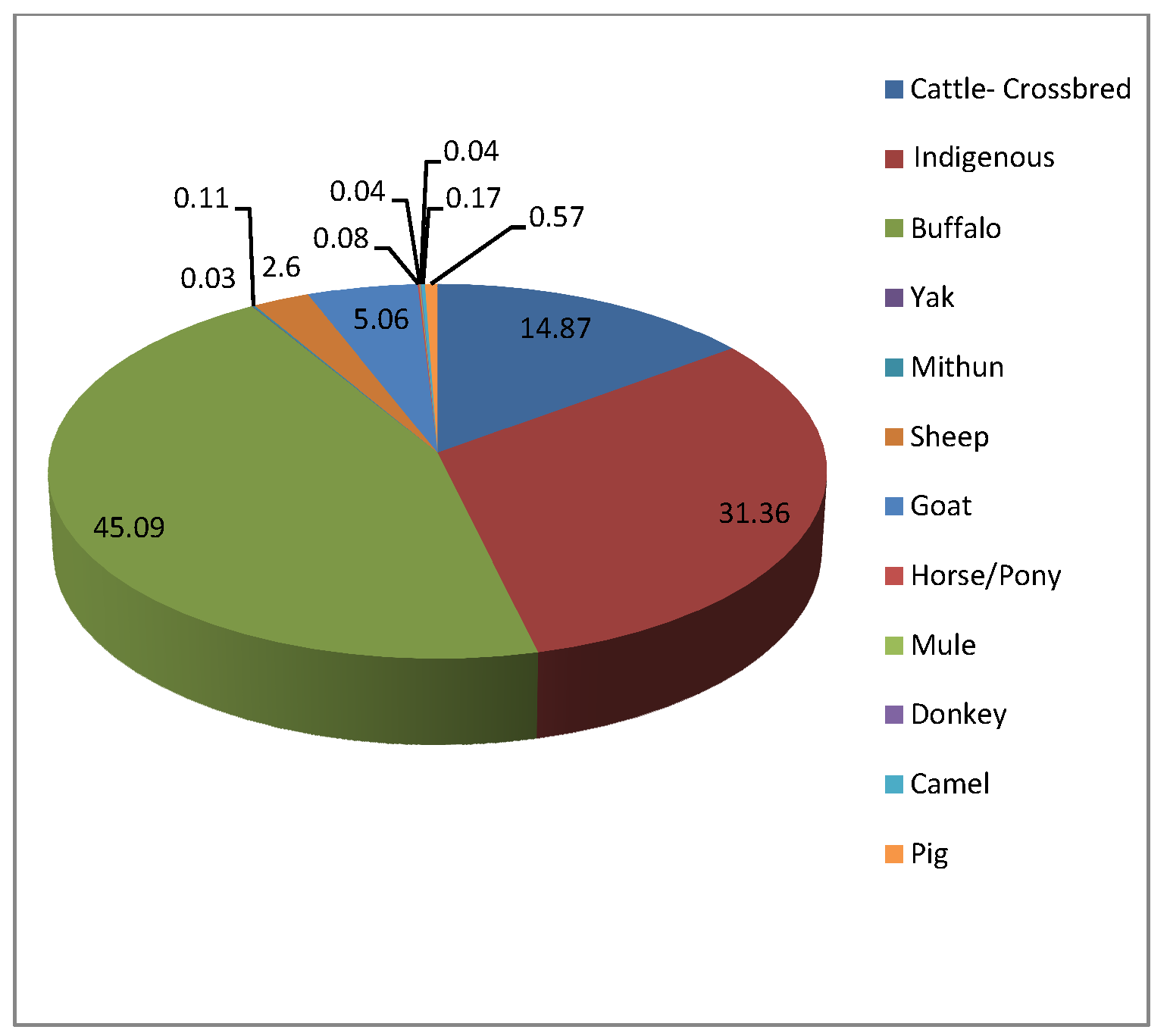



Livestock As Sources Of Greenhouse Gases And Its Significance To Climate Change Intechopen




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



State Of The Climate Bureau Of Meteorology




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Definition And Effect Medicsky




Greenhouse Gases Viztopia




What S In The Air Ucar Center For Science Education
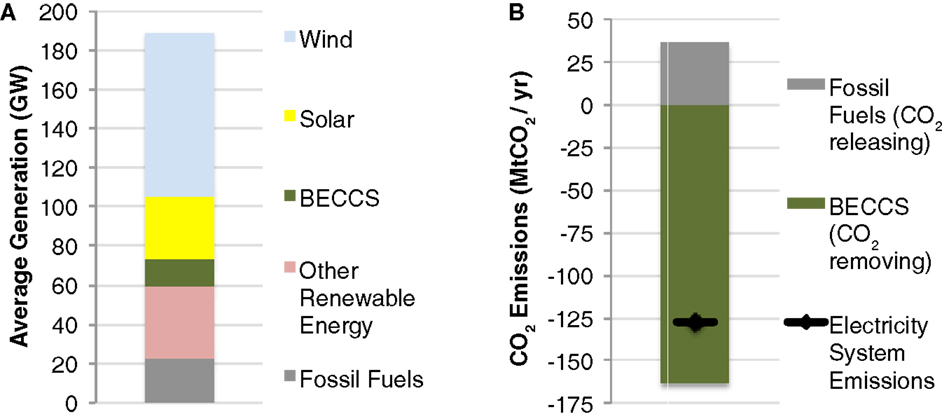



Removing Harmful Greenhouse Gases From The Air Using Energy From Plants Frontiers For Young Minds
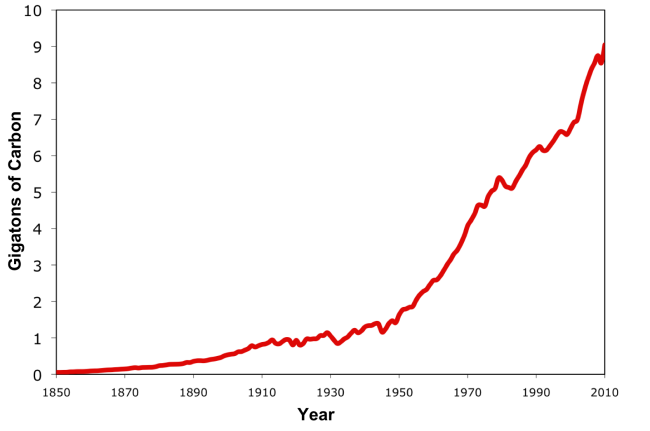



Noaa Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory
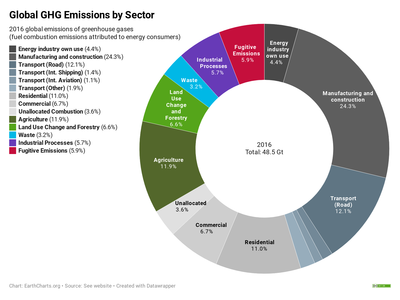



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
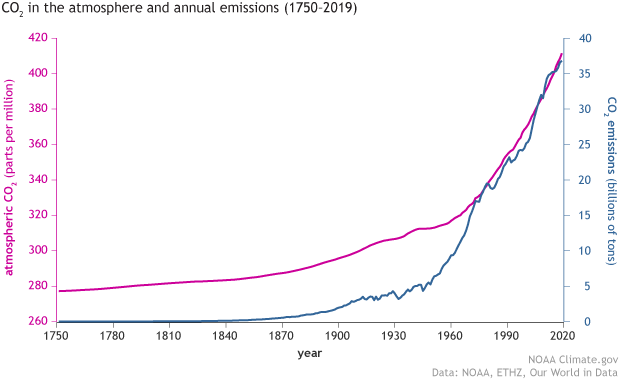



Climate Change Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Noaa Climate Gov




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Greenhouse Gas Emissions



How Much Greenhouse Gas Is In The Atmosphere Quora



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
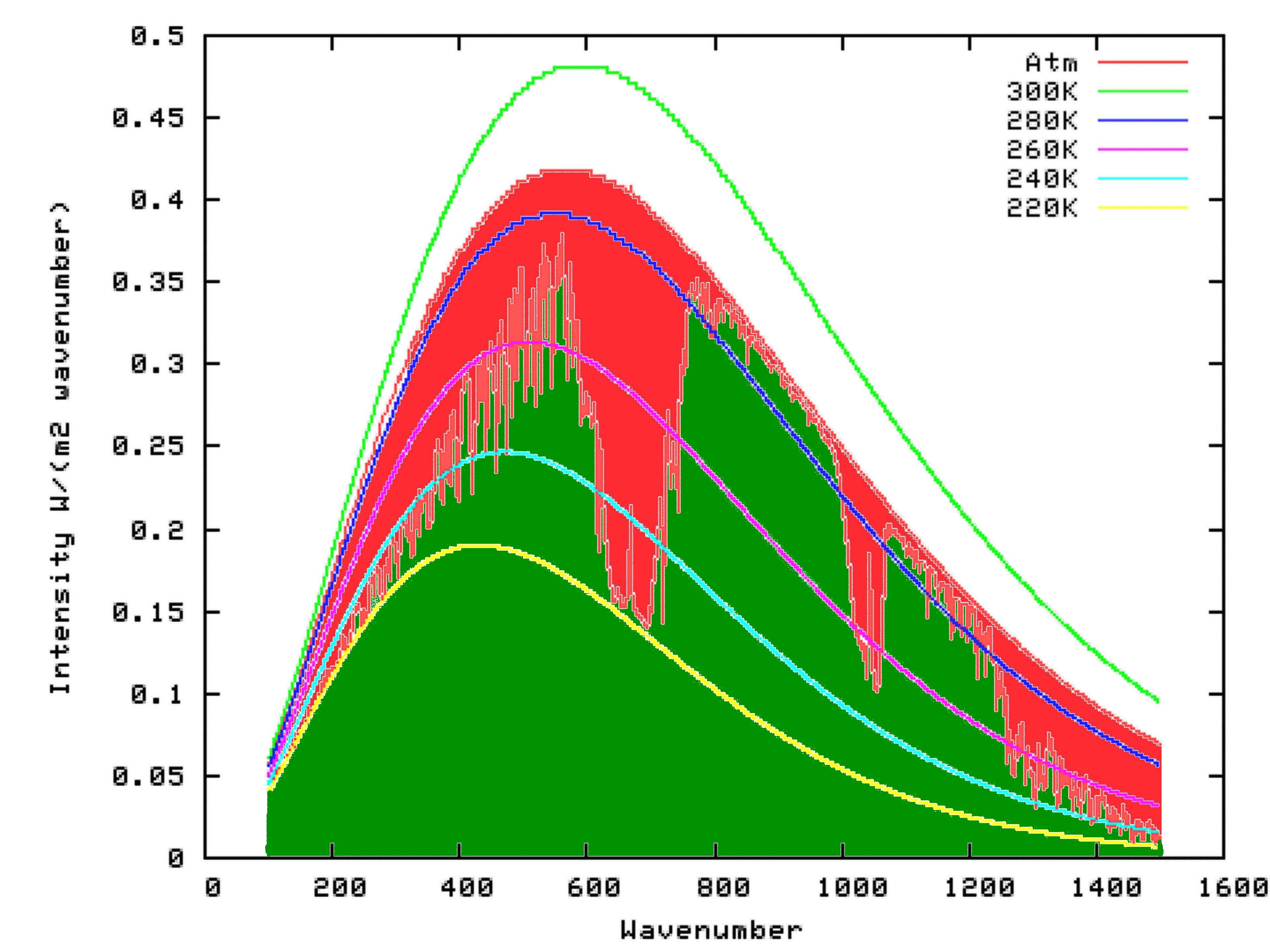



How Substances In Trace Amounts Can Cause Large Effects



Why Do We Need Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Quora




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
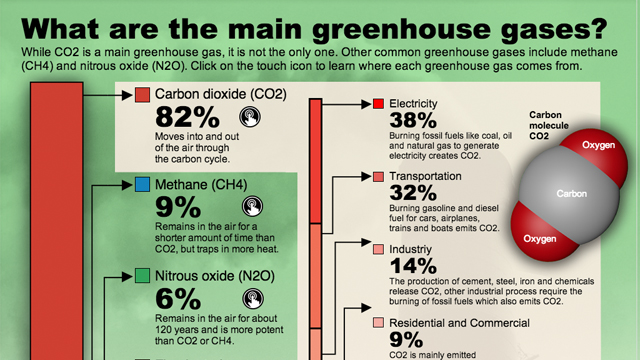



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Why Do We Need Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Quora



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
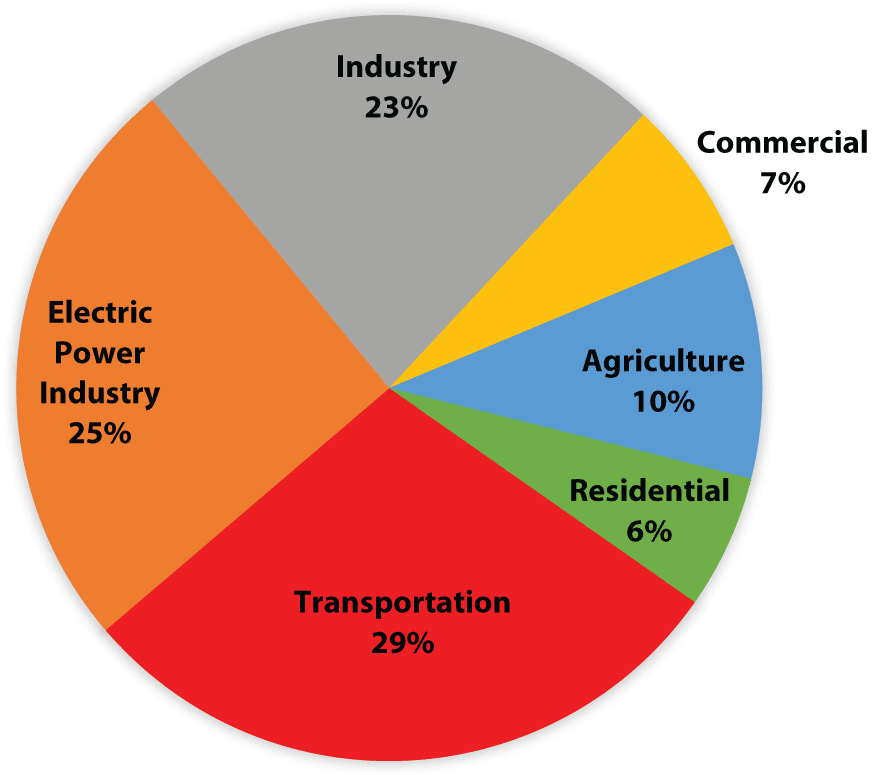



Agriculture And Greenhouse Gas Emissions G310 Mu Extension
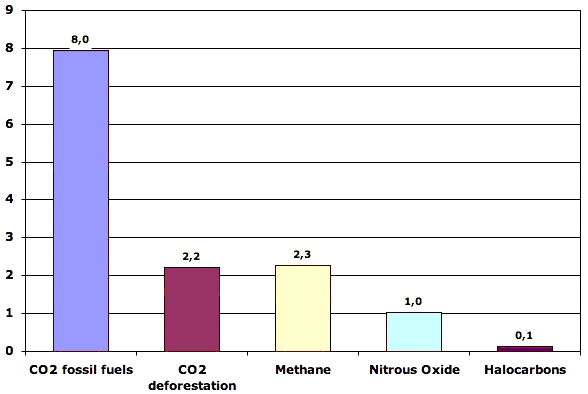



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja
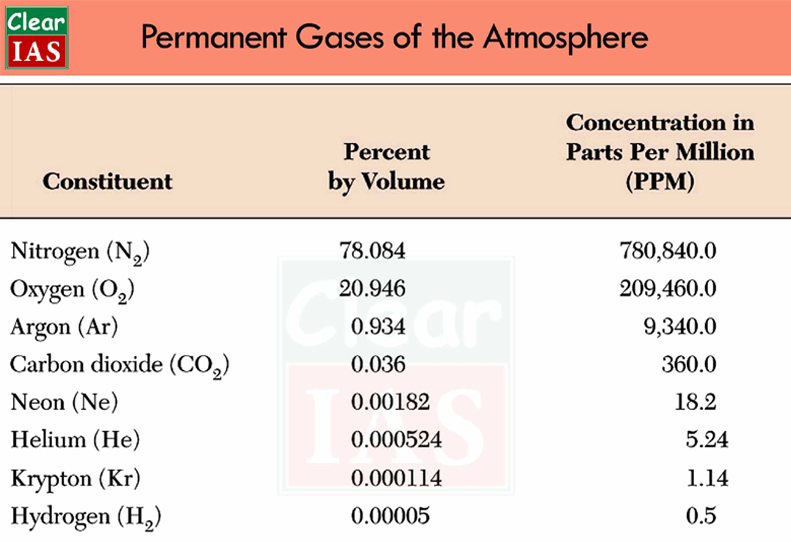



Composition And Structure Of The Earth S Atmosphere Clear Ias




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Why Do We Need Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Quora




Global Warming Radiative Forcing Britannica



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Cradle To Grave Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Dams In The United States Of America Sciencedirect



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
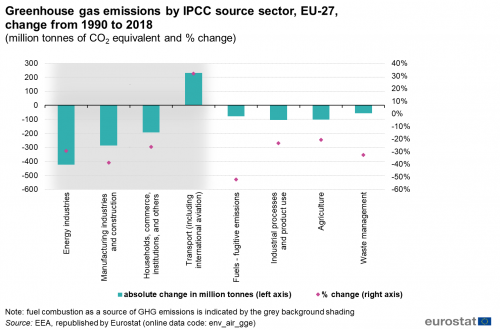



Climate Change Driving Forces Statistics Explained




What Is Nitrous Oxide And Why Is It A Climate Threat Inside Climate News




Global Warming How Does It Relate To Poultry Uga Cooperative Extension



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau
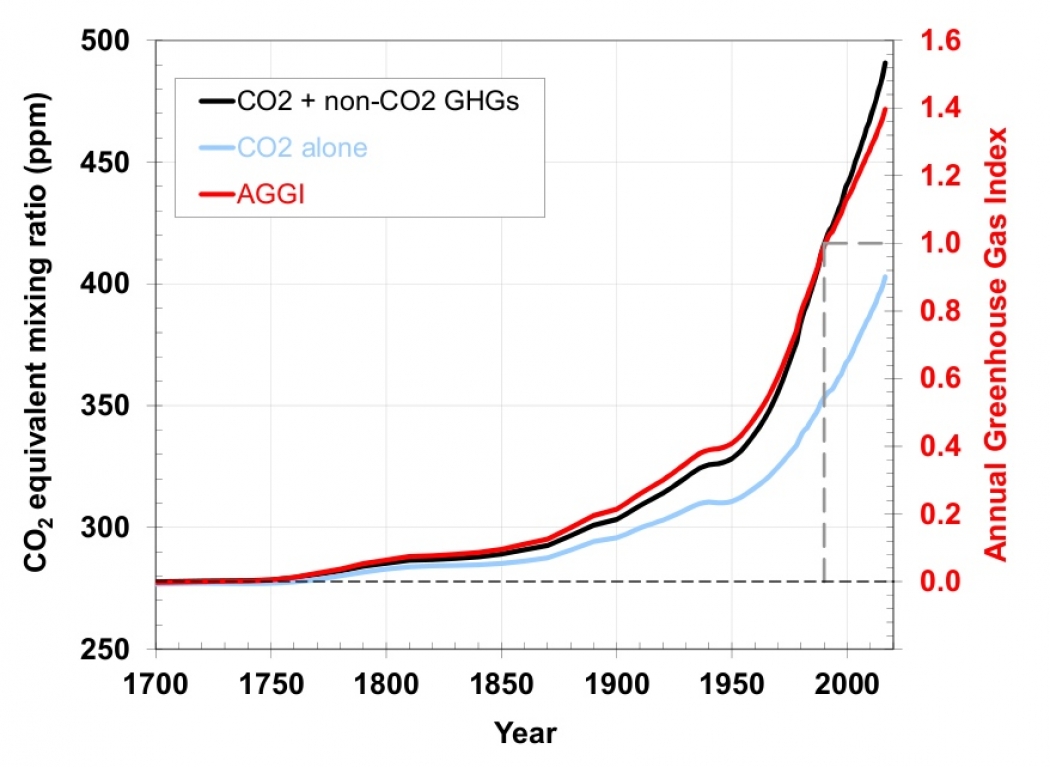



Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central



Why Do We Need Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Quora
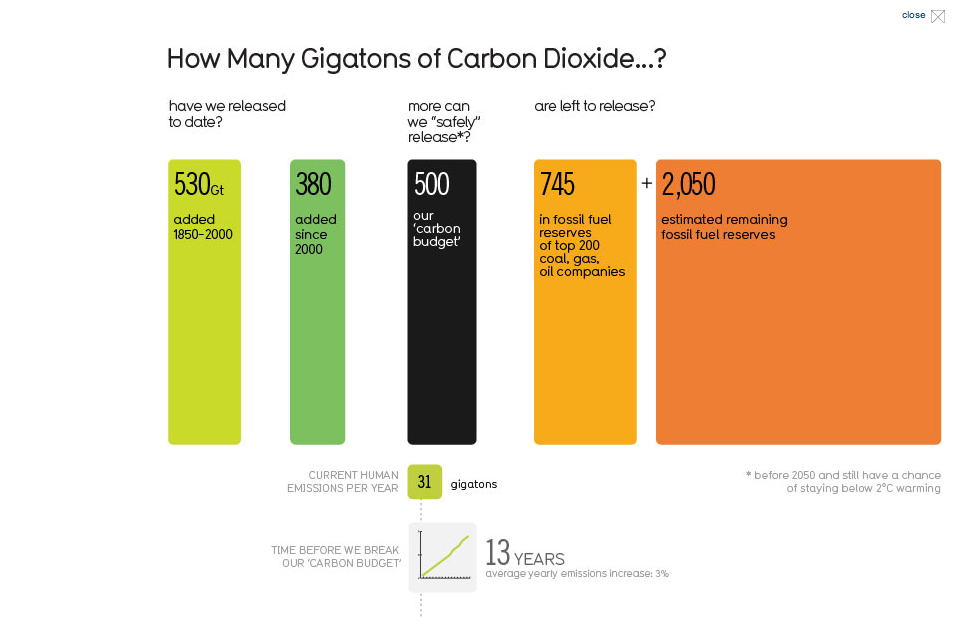



Doha Infographic Gets The Numbers Wrong Underestimates Human Emissions Carbon Brief




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



1




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization
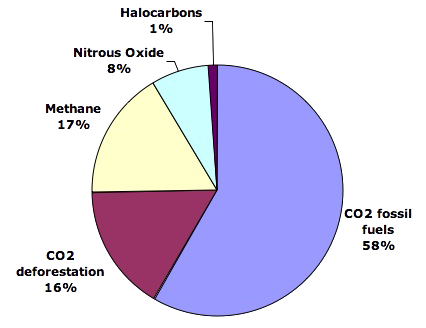



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
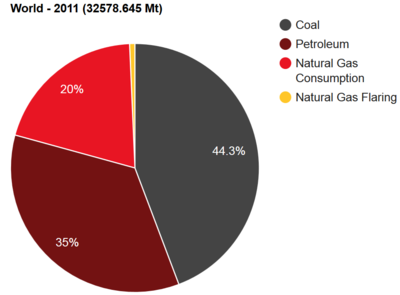



Flaring Energy Education




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef
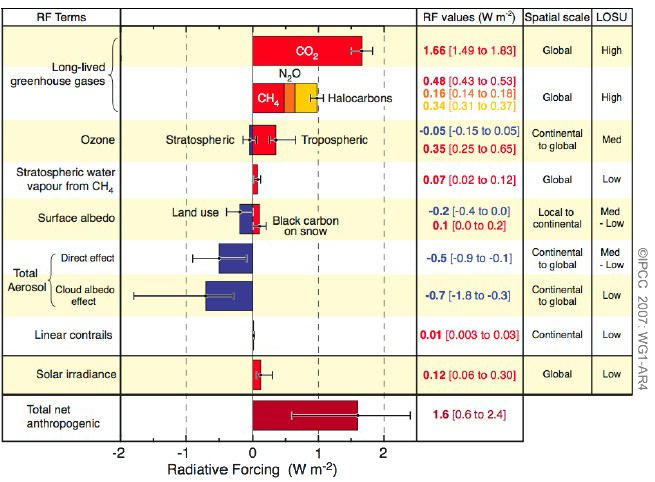



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici
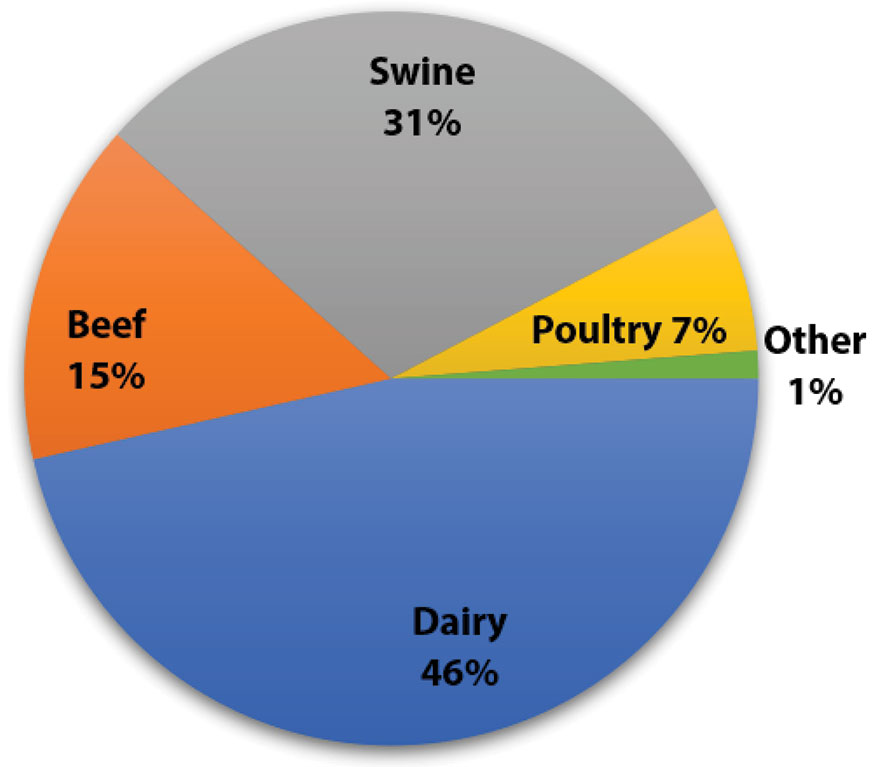



Agriculture And Greenhouse Gas Emissions G310 Mu Extension




Questions And Answers Ozone Secretariat



Forests And Climate Change
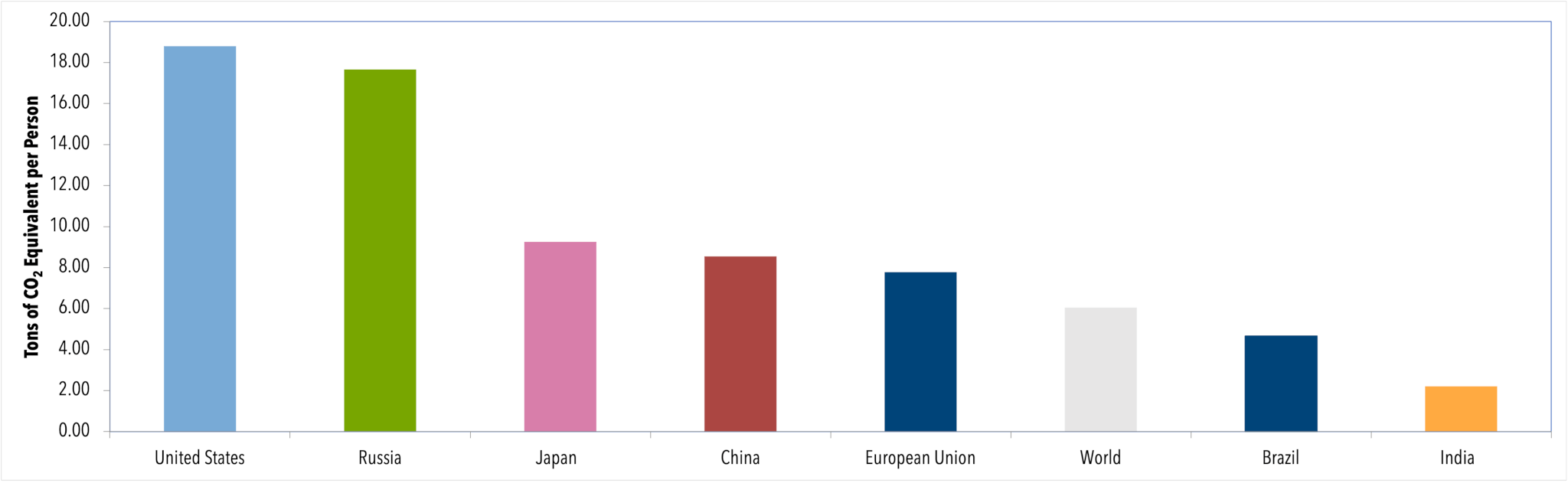



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
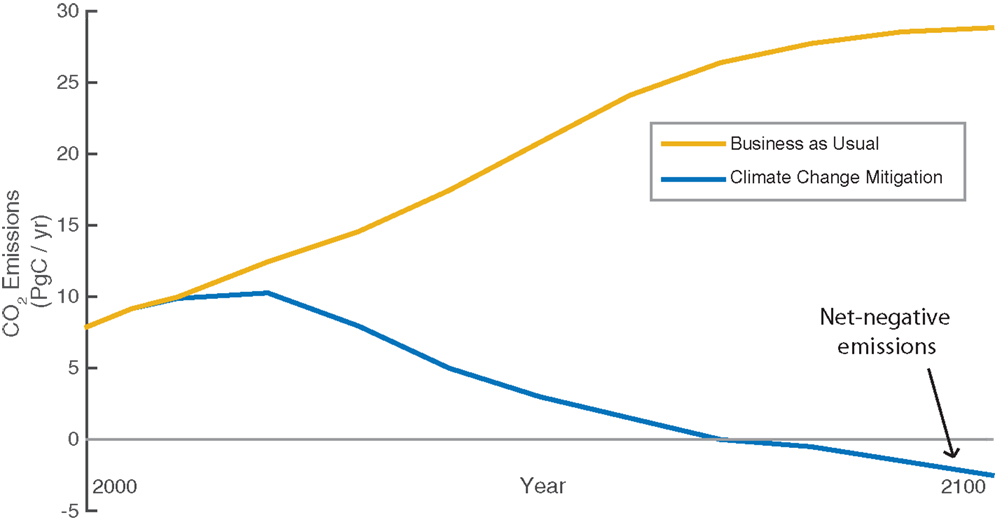



Removing Harmful Greenhouse Gases From The Air Using Energy From Plants Frontiers For Young Minds




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




K1 Psx4w2wnatm




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization
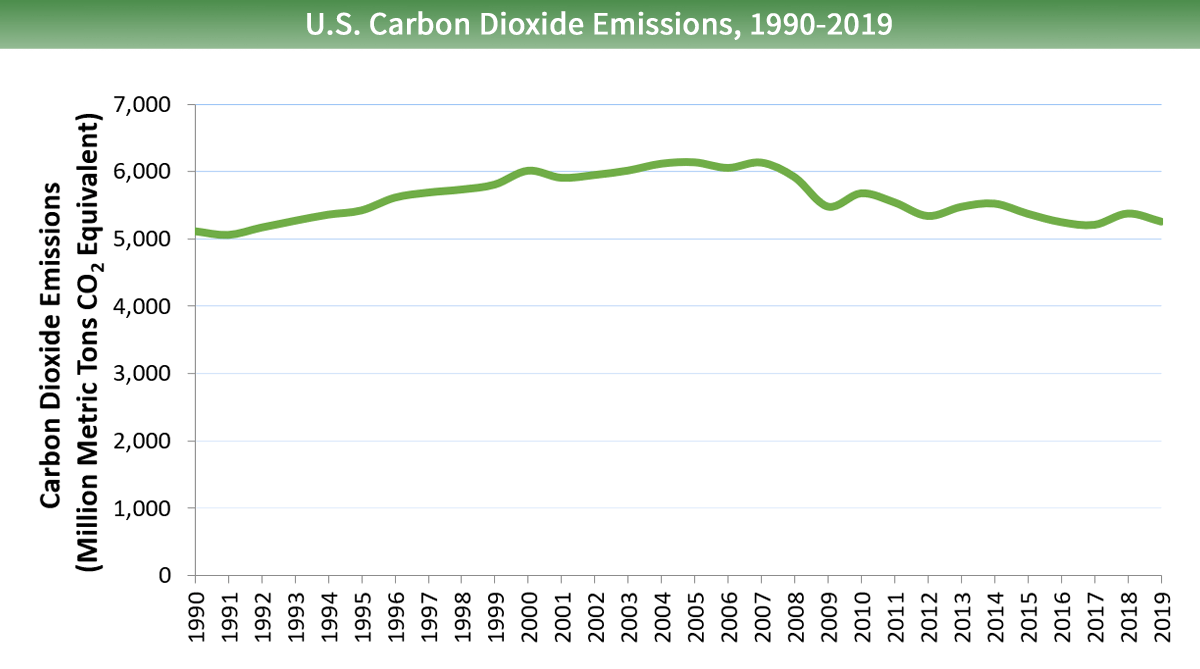



K1 Psx4w2wnatm
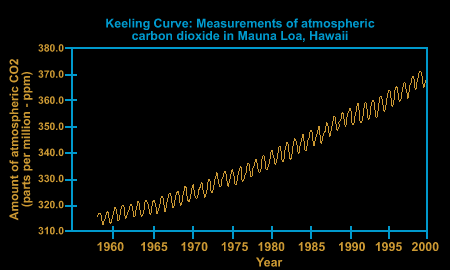



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
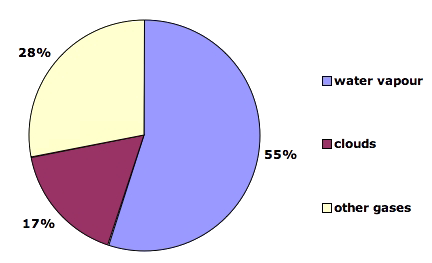



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus
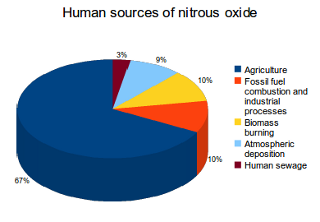



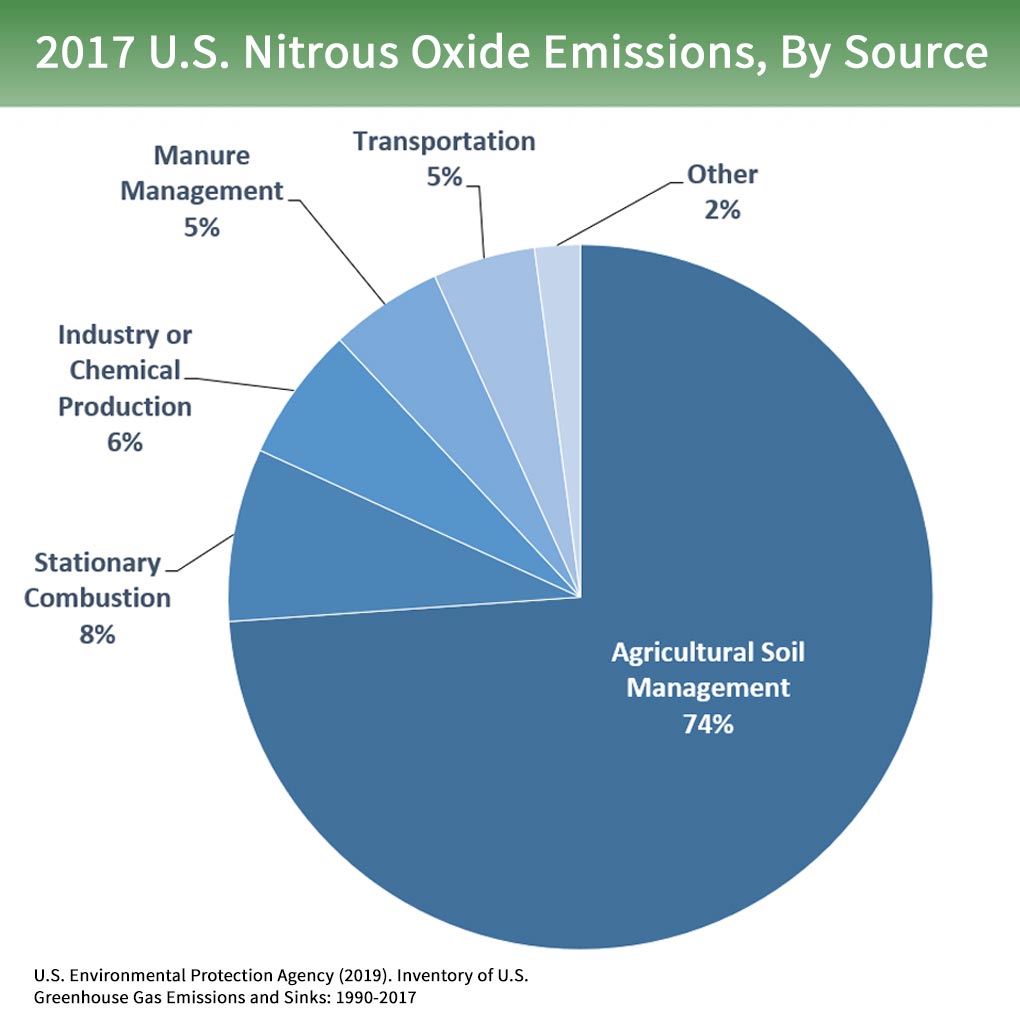
Main Sources Of Nitrous Oxide Emissions What S Your Impact




Atmosphere Of Earth Wikipedia




2 4 Carbon Flashcards Quizlet
.png)



Fact Sheet The Growth In Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Commercial Aviation White Papers Eesi




Composition Of Atmosphere Qs Study



Www Pbl Nl Sites Default Files Downloads Pbl Trends In Global Co2 And Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions 19 Report 4068 Pdf



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Component I A Personal Details Component I B Description Of Module Composition And Structure Of The Atmosphere Introducti



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿